What is the Peter Principle?
In the intricate dance of corporate dynamics, a phenomenon known as the Peter Principle often quietly unfolds, shaping the destiny of individuals within the organizational hierarchy. Coined by Canadian educator Laurence J. Peter, this principle posits that individuals in a hierarchy tend to rise to their “level of incompetence.” In simpler terms, employees get promoted until they reach a position where they’re no longer effective. This paradoxical predicament holds profound implications for organizational structures and employee management.
Understanding the Peter Principle:
At the heart of the Peter Principle lies a fascinating insight into the dynamics of career progression. As individuals excel in their current roles, they are rewarded with promotions. However, the skills that led to success in their previous roles might not necessarily align with the demands of the new position. Consequently, employees find themselves in roles where their competence no longer matches the requirements, leading to a plateau in performance.
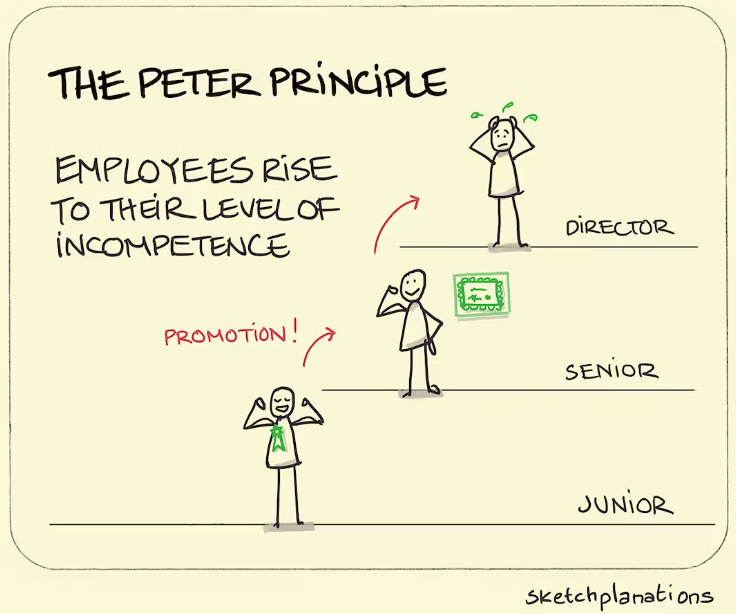
Applications in Corporate Realms:
The Peter Principle finds its manifestations in various facets of corporate life:
- Promotion Based on Current Performance:
- Employees are often promoted based on their success in their current roles rather than their aptitude for the new position.
- Impact on Team Dynamics:
- The misalignment of skills and responsibilities can affect team dynamics, hindering collaboration and productivity.
- Organizational Structure Challenges:
- As employees reach their levels of incompetence, organizational structures may become top-heavy, impacting overall efficiency.
Mitigation Strategies:
Recognizing and addressing the Peter Principle is crucial for maintaining a healthy organizational structure. Strategies include:
- Continuous Skill Assessment:
- Regularly assess and align employees’ skills with the requirements of their roles.
- Training and Development:
- Invest in training programs to equip employees with the skills needed for their current and potential future roles.
- Transparent Communication:
- Foster a culture of open communication where employees and management can discuss career aspirations and potential challenges.
Real-World Example: The Case of Sarah Thompson
In a mid-sized technology firm, Sarah Thompson was a brilliant software engineer known for her technical prowess. Her coding skills and problem-solving abilities were unparalleled, making her an invaluable asset to the development team. Recognizing her exceptional performance, the company decided to promote Sarah to a managerial role, where she would oversee a team of software engineers.
However, as Sarah transitioned into her new position, challenges emerged. While her technical acumen was unquestionable, the demands of managerial responsibilities required an entirely different skill set—effective communication, team leadership, and project management. Sarah, despite her brilliance in coding, found herself struggling to navigate the complexities of interpersonal dynamics, project timelines, and strategic planning.
The consequence was twofold. First, Sarah’s team, once a cohesive and efficient unit, experienced a decline in productivity due to the mismatch between her technical expertise and the managerial demands. Second, Sarah, despite her best intentions, faced mounting stress and frustration in her role, leading to a decline in job satisfaction.
Sarah’s case vividly illustrates the pitfalls of the Peter Principle, where an individual’s excellence in a specific role does not guarantee success in a higher, more complex position. This real-world scenario underscores the importance of aligning promotions with the holistic skill set required for the new role, thereby mitigating the potential negative effects of the Peter Principle in organizational dynamics.
Conclusion:
In the ever-evolving landscape of corporate dynamics, the Peter Principle serves as a cautionary tale. Navigating the delicate balance of career progression requires a strategic approach that goes beyond promoting individuals solely based on their current achievements. By embracing continuous learning, transparent communication, and thoughtful skill assessments, companies can mitigate the effects of the Peter Principle, fostering a culture of sustained growth and effectiveness. In the end, it’s not just about climbing the corporate ladder; it’s about ensuring each step is taken with competence and strategic foresight.
You can find the book here. https://a.co/d/0BQ19ZW: The Peter Principle in Companies