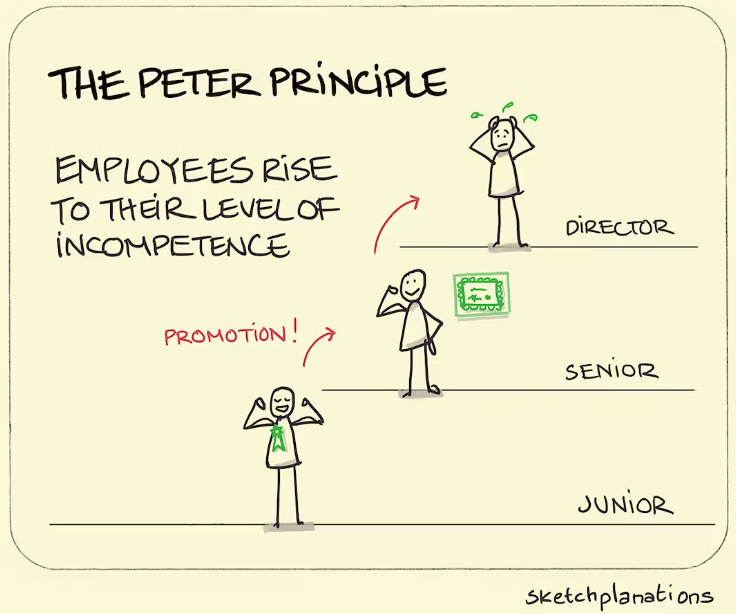
In today’s society, certain systems that form their backbone exhibit alarming cracks, raising questions about their effectiveness and relevance. From the realms of education to healthcare and finance, it becomes evident that these systems, once revered, are now fraught with shortcomings, leaving individuals grappling with the consequences. Let’s delve into the core issues plaguing these vital pillars of society.
The Broken Education System:
Entering the corridors of education, a glaring issue emerges—the misalignment between traditional academic pursuits and real-life skills. Students invest in education, often burdened by exorbitant costs, only to find a mismatch between what they learn and the practical skills required in the workforce. The overvaluation of degrees and the neglect of essential life skills contribute to a system that fails to prepare individuals adequately for the challenges beyond the classroom.
The Fractured Healthcare System:
The seismic shockwaves of the COVID-19 pandemic laid bare the vulnerabilities of healthcare systems worldwide. The unpreparedness, overwhelmed facilities, and inadequate response highlighted systemic flaws. From insufficient resources to lack of coordination, the health system’s brokenness became painfully apparent, prompting a critical examination of its structure and functionality.
The Enigmatic Financial System:
Entering the complex world of finance, the opacity of the financial system becomes a pressing concern. Only a select few truly understand its intricate workings, leaving the majority exposed to the whims of volatility and economic downturns. The aftermath of financial crashes underscores the fragility of a system where the consequences of decisions made by a privileged few reverberate through the lives of the masses.
Common Threads of Dysfunction:
Despite the apparent differences in these systems, common threads of dysfunction emerge. Lack of transparency, disproportionate distribution of benefits, and a growing disconnect between the systems and the individuals they are meant to serve contribute to a sense of disillusionment and frustration.
Challenging the Status Quo:
As we confront the realities of broken systems, there arises an urgent need to challenge the status quo. Calls for educational reforms emphasizing practical skills, a resilient healthcare system prepared for unforeseen challenges, and a financial system that prioritizes the well-being of all citizens resonate as crucial steps toward building more robust and equitable foundations.
Conclusion:
In the face of these broken systems, individuals and societies stand at a crossroads, presented with an opportunity to reevaluate and redefine the structures that shape our lives. Addressing the flaws in education, healthcare, and finance requires collective introspection and concerted efforts to forge systems that truly serve the well-being and progress of all.